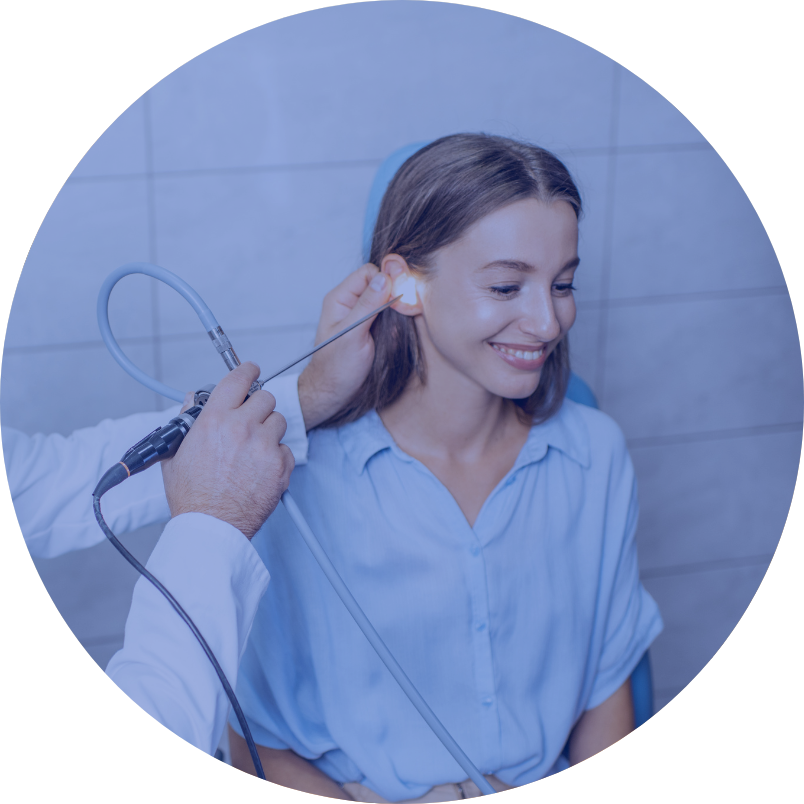
Tympanic membrane and ossicle reconstruction


OPERATIONS
Tympanic membrane and ossicle reconstruction Middle ear surgery for inflammatory lesions or cholesteatoma FESS – Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Nasolacrimal duct obstruction Tonsillotomy – “trimming” of palatine tonsils Middle ear tube surgery Adenoidectomy removal of the pharyngeal tonsil Tonsillectomy – removal of palatine tonsils Septoplasty Correction of nasal septum deformityOPERATIONS
Perforation of the tympanic membrane can stem from inflammation or trauma. Damage to the tympanic membrane can also lead to damage to the ossicles. The symptoms of these conditions include hearing loss caused by impaired conduction of sound in the middle ear. It may be accompanied by tinnitus and recurrent ear discharge, especially after it becomes wet.
The procedure of myringoplasty, or tympanic membrane plasty, involves filling the defect with the patient’s own tissue, usually cartilage from the ear auricle or the prefascial lamina of the temporal muscle. The incision is made inside the ear canal or behind the ear auricle. There are several techniques for filling a tympanic membrane defect, depending on its size and location.
Ossiculoplasty is a procedure to reconstruct the ossicular chain and can be performed together with myringoplasty. In addition to the patient’s own material (cartilage or compact bone), prostheses made of biocompatible materials are used for reconstruction. The dressing is removed from the ear one week after the procedure.
Preoperative instructions:
- Full blood count
- Coagulation pathways
- Electrolytes, CRP
- Blood type
Postoperative instructions:
- Avoid physical strain
- Keep the ear dry
- Use painkillers

