Adenoidectomy removal of the pharyngeal tonsil


OPERATIONS
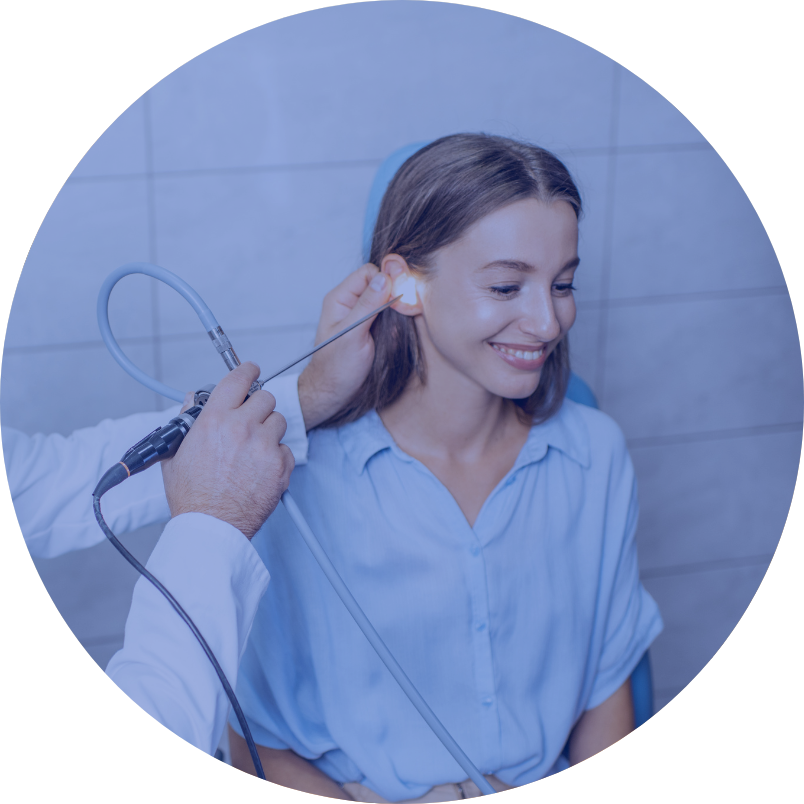
Tympanic membrane and ossicle reconstruction Middle ear surgery for inflammatory lesions or cholesteatoma FESS – Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Nasolacrimal duct obstruction Tonsillotomy – “trimming” of palatine tonsils Middle ear tube surgery Adenoidectomy removal of the pharyngeal tonsil Tonsillectomy – removal of palatine tonsils Septoplasty Correction of nasal septum deformityOPERATIONS
The pharyngeal tonsil (i.e., the third tonsil) is a cluster of lymphatic tissue located on the roof of the nasopharyngeal (behind the nasal cavity and above the soft palate). Physiological enlargement of the pharyngeal tonsil occurs between 3 and 7 years of age and is associated with the process of acquiring immunological competence by the child. Pathological (excessive) hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil is most often caused by frequent infections of the upper respiratory tract. Genetic tendencies to hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsils and an allergic component are also observed.
The main symptom of hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil is nasal obstruction, manifested by difficulty in its cleansing, resulting in chronic or often recurrent rhinitis and increased susceptibility to respiratory infections. In addition, due to obstruction of the upper respiratory tract, the child maintains an open mouth and breathes through it, with additional snoring at night, which can even lead to apnea.
Untreated hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsils, in addition to frequent infections of the respiratory tract and apnea, leads to obstruction of the ear trumpets, with their outlet located on the lateral nasopharynx wall. As a result of formation of negative pressure in the middle ear, there is accumulation of fluid in the tympanic cavity and hearing loss occurs.
Adenoidectomy is performed under general anesthesia. It consists in removing the lymphatic tissue of the nasopharynx with approach through the mouth. The patient is usually discharged home on the day of the procedure. Laryngological examination is recommended on the first day after surgery and after 7-14 days. It is recommended the child does not go to kindergarten/school for a week after adenoidectomy.

