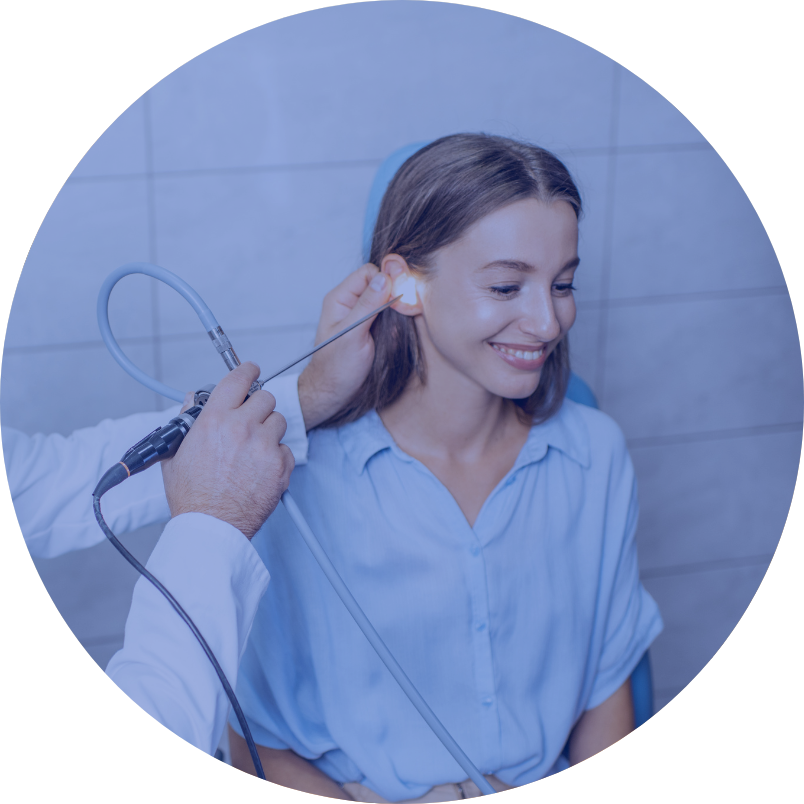
Middle ear surgery for inflammatory lesions or cholesteatoma


OPERATIONS
Tympanic membrane and ossicle reconstruction Middle ear surgery for inflammatory lesions or cholesteatoma FESS – Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Nasolacrimal duct obstruction Tonsillotomy – “trimming” of palatine tonsils Middle ear tube surgery Adenoidectomy removal of the pharyngeal tonsil Tonsillectomy – removal of palatine tonsils Septoplasty Correction of nasal septum deformityOPERATIONS
Recurrent acute inflammation or untreated exudative otitis media leads to chronic inflammation manifested by ear discharge and hearing loss. Over time, dizziness, facial nerve palsy or meningitis may occur.
Middle ear cholesteatoma is a type of inflammation in which a tumour composed of infected cornified multilayer squamous epithelial cells has formed. This tumour is non-responsive to drug treatment, while its growth causes destruction of the surrounding bone tissue. Surgical treatment is then necessary.
The operation involves removing inflammatory lesions from the mastoid process and the tympanic cavity. The incision is made behind the ear auricle. Subsequently, using a surgical drill, the bone of the mastoid process is milled, and the inflammatory lesions contained therein are removed. During the procedure, it may be necessary to remove inflamed ossicles from the tympanic cavity. Ossicle reconstruction can be performed during the same surgery or at the second stage.
Preoperative instructions:
- Full blood count
- Coagulation pathways
- Electrolytes, CRP
- Blood type
Postoperative instructions:
- Avoid physical strain
- Keep the ear dry
- Use painkillers

